Real estate investing is not only one of the safest investments you can make, but it also has many benefits, including appreciation, tax advantages, and the ability to earn passive income. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of real estate investments and the pros and cons of each. A good starting point is to look at indirect versus direct real estate investments.
Indirect Real Estate Investments
An indirect real estate investment means you don’t directly own the property, reducing the risk and the effort required. While the profits are lower, they can be a good starting point for those just starting to build their portfolio. Seasoned investors also like them because they are a good way to diversify their portfolios and hedge against market fluctuations.
REITs and crowdfunding platforms can be the best route for real estate investors looking for more passive investments.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
A REIT is a company that owns, manages, or finances income-producing properties. To be legally classified as a Real Estate Investment Trust, the company must distribute at least 90% of its income to its investors.
They are generally not taxed like corporations, which provides tax benefits to both individual investors and the company. At the same time, though, the dividends may be taxed more than a direct investment in commercial or residential real estate, reducing your profits.
Typically, these companies have a diversified portfolio of different properties, such as office buildings, shopping centers, apartment buildings, or hotels. They generate rental income and distribute it to investors as dividends.
Most REITs operate like stocks, meaning they are traded on the New York Stock Exchange or other exchanges. This enables the general public to access a portion of ownership in large purchases such as hotels or condominiums.
A REIT can be a great option for your investment portfolio if you don’t have the capital to purchase rental property on your own but still want to benefit from the security and passive income from real estate. They are also more liquid than purchasing commercial real estate, making them less risky for an investor.
Pros of Publicly Traded REITs:
|
Cons of Publicly Traded REITs:
|
Crowdfunding
The idea behind real estate crowdfunding is to pool money to fund a project. This offers investors the ability to become shareholders in properties with smaller initial amounts and provides companies access to different kinds of capital. It also means that investors can enjoy some of the profits without dealing with the headaches of managing properties.
With this option, you’ll find real estate investment groups that advertise their upcoming projects on a crowdfunding platform. The listing will include information like property type, potential return on investment, risks, and funding needs. You’ll then put down money upfront, and the developer will transform raw land into a new property.
Once the funding goal is met and the rental property is ready, the group will manage the property and provide regular updates on its profitability — and dividends to the investors.
In many cases, real estate crowdfunding platforms put money into real estate investment trusts or similar investments. The most common option is private REITs, which aren’t available to anyone but the investors.
Passive real estate investments like this can provide you with extra cash flow, though it’s not as generous as other asset classes, such as financing an entire rental property with your own money.
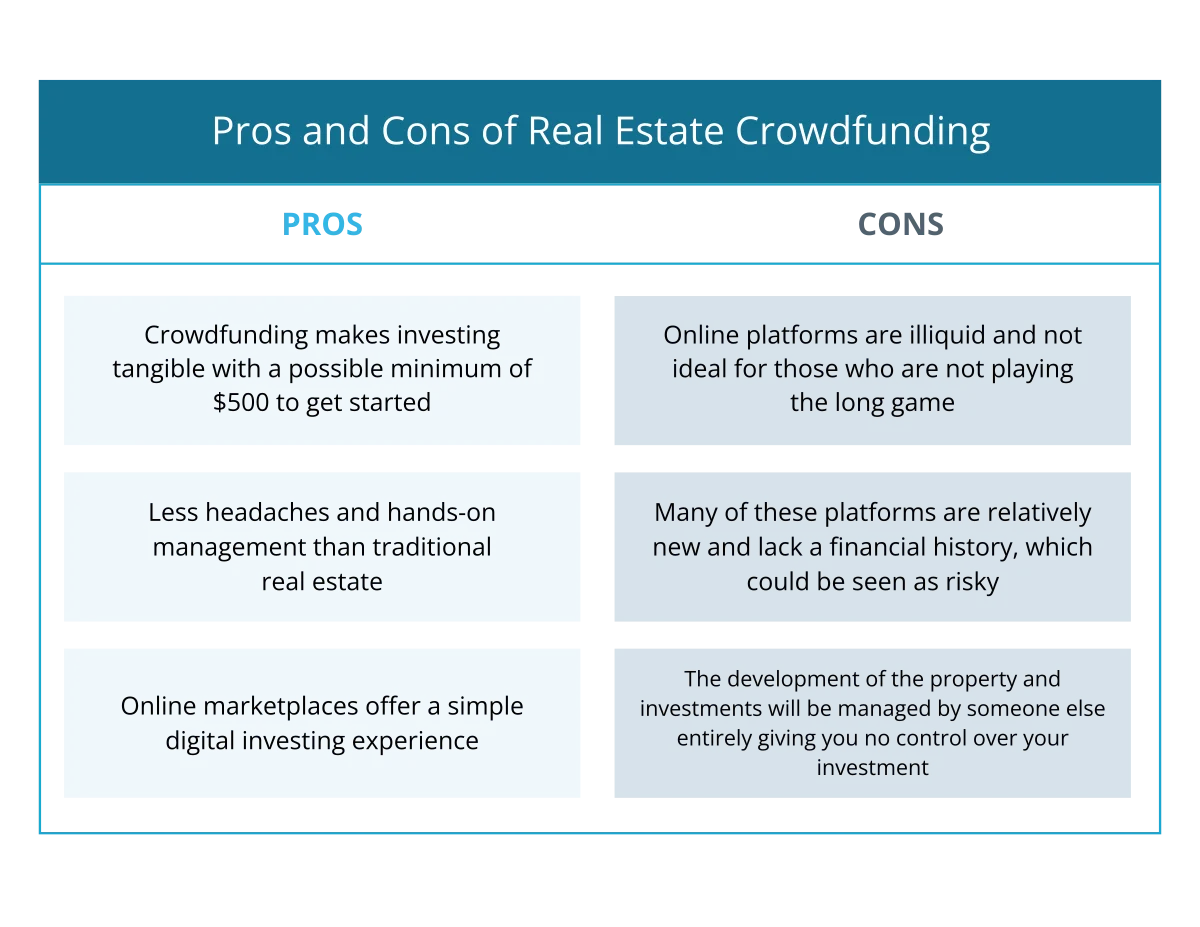
Pros of Real Estate Crowdfunding
|
Cons of Real Estate Crowdfunding
|
Direct Real Estate Investments
A direct real estate investment is when you have direct ownership of the asset. An example is purchasing an apartment complex and managing it yourself. These give you more control over what happens with your money, but it also requires a lot of hard work and can be risky. Let’s take a more comprehensive look at what these investments look like.
Commercial Real Estate Investments
In simple terms, commercial properties are properties with five units or more or properties rented out to businesses. Each property will be populated by a tenant, who will then pay rent on their particular unit to help finance the overall mortgage.
In commercial real estate buildings, you may have certain units that are specialized for particular tenants, such as small restaurants or stores. Some even may have medical centers, like a dentist’s office. This gives you several smaller niches within your overall real estate investment, which can make it easier or harder to attract tenants when one leaves.
With others, such as apartment complexes, almost all the units will be identical. This can make management and maintenance easier, as well as streamline the tenant advertising aspect.
There are many commercial property types, including:
- Multifamily properties: A residential property with five or more rental units.
- Mixed-use properties: A mix of residential and commercial units. An example is a restaurant on the ground floor with apartments on top.
- Retail space: A rental building that is occupied by retail establishments, such as a clothing store. The familiar strip mall is a perfect example of commercial real estate.
- Office building: A commercial space with tenants operating a business, such as a call center.
- Industrial real estate: It can include warehouses and buildings with a manufacturing or assembly space.
- Flex space: A mixed-use property typically where there is a combination of office and warehouse space.
- Self-storage: A special building designed with small bays that are leased for the storage of personal items.
The primary benefit of commercial real estate is that you have a steadier cash flow. Even if one unit sits vacant, you will still be collecting rent from the other tenants, making you less likely to default than with a single-family residential property. However, there are other benefits as well — and some downsides.
Pros of Commercial Real Estate Investments
|
Cons of Investing in Commercial Real Estate
|
Residential Real Estate Investments
A single-family residential investment property is a single-family residence that is not owner occupied. There are many ways to invest in residential real estate. Here is an overview of the types of residential real estate investments.
Long-Term Rental Properties
A long-term rental property is a single-family home a landlord will rent out long term. This asset class offers steady rental income and many tax benefits.
Some of the drawbacks include the time commitment and headaches associated with managing a property. If your tenant leaves, you will lose your cash flow and will need to finance the mortgage without the rent income.
Many real estate investors hire property managers to assist with tasks such as collecting rent and handling maintenance. While this does cut into profits, it also ensures compliance with legal obligations and encourages tenants to stay longer.
Short-Term Rentals
Vacation rentals are residential properties investors rent out for the short term. These real estate investments provide a much higher rent potential than long-term rentals.
You can also charge different rates throughout the year, capitalizing on seasonal trends in your area and boosting your income potential. Particularly lucrative areas can make you hundreds of dollars per night, especially if you have great marketing.
At the same time, you have more expenses, such as frequent cleanings and higher marketing costs. Occupancy is also generally lower, so you must carefully budget your profits and prepare for seasonal lulls. Many property owners outsource the management to a property manager.
Rehabbing Properties
Buy-and-hold real estate investments are income-producing real estate assets that investors hold onto in their investment portfolios. By contrast, flipping houses is a real estate investing strategy designed to make lots of money at one time. A real estate investor will purchase a physical property that needs major repairs, renovate it, and sell it.
If you’re buying a distressed property for cheap, you’ll need to spend a lot of money and time getting it up to a sellable standard. This involves a great network of contractors and, often, some construction knowledge of your own.
It’s not uncommon for house flips to go over budget, necessitating more funds. While the earning potential is huge, this strategy requires money upfront and is often financed by hard money loans.
Your ability to flip a house is also heavily dependent on the real estate market. You may find that the demand isn’t there when you’re ready, and the property will spend several months on the market, forestalling your return on investment. Often, investors will work with a real estate agent to ensure a smooth and profitable real estate transaction.
Wholesaling Properties
Real estate wholesalers sell properties quickly to interested parties before the original contract goes through. This means you’re not selling the property itself, just the right to purchase it.
In essence, you find an undervalued property, convince the seller to let you put it under contract, and then find an interested buyer. The difference between what you put down to secure the contract and what you charge to your buyer is called the wholesale fee. Generally, this is about 5% to 10% of the original purchase price.
Your actual engagement with the physical property is minimal with real estate wholesaling. You’re not as responsible for building repairs as you would be for house flipping or holding a long-term real estate investment.
When done correctly, wholesalers can get quicker returns on investments without worrying about construction or improvements.
One drawback is the quick turnaround time to find a buyer. To make this investment strategy work, you’ll need a strong network of helpful real estate agents and potential buyers, which means it’s not the best investment strategy for those new to the industry.
Residential Real Estate Investing Pros
|
Residential Real Estate Investing Cons
|
Raw Land
Another type of direct investment is purchasing undeveloped land to either sell to real estate developers or develop yourself. You may also hold it in your real estate portfolio for a time, waiting for the land value to increase, at which point you could sell it or build an investment property.
As an example, a nearby suburb could expand, and developers could seek new places for an apartment complex, which will ensure that the property sells for much more than you paid for it. If you’re confident in your own cash flow, you could build your own rental properties and generate income from new tenants moving into the area.
Vacant land can have many possibilities — for example, you could convert it into industrial real estate investments — but you need to do your homework and ensure that you have the property zoning for what you’d like to build.
As these real estate investment types require little more paying property taxes, land investments can be a relatively low-effort investment strategy. However, they also won’t generate much income until you sell or develop the property.
Pros of Raw Land
|
Cons of Raw Land
|
Which Real Estate Investment is Right for You?
The best investment strategy for you is one that has an acceptable risk level, cash flow, and time and money investment for your needs. Some people prefer the hands-on excitement of house flipping, while others want more passive real estate investments such as REITs.
It’s best to learn all you can about each type of real estate investment so that you can match your choice to your risk profile.
Ready to gain financial independence through real estate? Visio Lending can help. We’re a specialized private lender that works exclusively with real estate investors, helping them obtain the funding they need to develop a strong cash flow. We offer flexible loan terms, competitive interest rates, and a streamlined process that helps you quickly make the best investments.
Contact us today to learn more about our options and find out how you can make your money work harder through smart rental investments.